VIX: The Ultimate Guide To Understanding Volatility Index And Its Role In Financial Markets
Alright folks, let’s dive straight into the heart of financial markets and unravel the mystery behind the VIX. If you’ve ever heard traders and analysts throwing around terms like “fear gauge” or “investor anxiety meter,” chances are they were talking about the Volatility Index, or simply VIX. It’s not just a number on a screen—it’s a powerful tool that can help you make smarter decisions in the world of finance. So, buckle up because we’re about to take a deep dive into what the VIX is, how it works, and why it matters.
Now, before we get too technical, let’s set the stage. Imagine the stock market as a rollercoaster ride. Sometimes it’s smooth sailing, but other times it feels like you’re plummeting at 100 miles per hour. The VIX is like the ride operator who tells you how wild the ride is going to be. It measures market volatility, which basically means how much prices are expected to swing up or down. And trust me, knowing this can save your portfolio from a major meltdown.
But why should you care? Well, understanding the VIX isn’t just for seasoned investors or Wall Street elites. It’s for anyone who wants to navigate the choppy waters of the financial markets with confidence. Whether you’re a newbie investor or a seasoned pro, this guide will give you the tools and insights you need to make sense of the VIX and use it to your advantage. So, let’s get started!
Read also:Steve Sullivan Katv The Unsung Hero Of Arkansas Journalism
Here’s a quick overview of what we’ll cover:
- What is the VIX?
- A Brief History of the VIX
- How is the VIX Calculated?
- The Role of VIX in Financial Markets
- Using the VIX for Trading
- The Impact of VIX on Investor Sentiment
- Why VIX is Called the Fear Gauge
- Strategies for Leveraging the VIX
- The Future of VIX in Modern Finance
- Wrapping It Up: Why the VIX Matters
What is the VIX?
Alright, let’s start with the basics. The VIX, short for Volatility Index, is a real-time measure of market expectations of near-term volatility. It’s essentially a prediction of how much the S&P 500 index is expected to move over the next 30 days. Think of it as the market’s crystal ball, giving you a glimpse into what might happen in the near future.
Now, here’s the kicker: the VIX doesn’t actually predict whether the market will go up or down. What it does is tell you how much movement—up or down—is expected. So, if the VIX is high, it means the market is bracing for some serious ups and downs. On the flip side, a low VIX suggests that things are pretty calm and predictable.
And why is this important? Well, as an investor, knowing the level of volatility can help you adjust your strategy. Are you feeling adventurous and ready to take on some risk? Or do you prefer to play it safe and protect your assets? The VIX can be your guide in making those decisions.
A Brief History of the VIX
Let’s rewind the clock a bit. The VIX was first introduced by the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) back in 1993. At the time, it was a groundbreaking concept that gave investors a new way to gauge market sentiment. Before the VIX, traders had to rely on gut feelings and anecdotal evidence to predict market moves.
But the VIX wasn’t always the same as it is today. In 2003, the CBOE updated the methodology to better reflect the options market. This new version, often referred to as VIX2, is the one we use now. And boy, has it become popular! Today, the VIX is one of the most widely followed indicators in the financial world.
Read also:Durins Day Lotro A Celebration Of Dwarven Heritage And Lore
Why Was the VIX Created?
So, why did the CBOE bother creating the VIX in the first place? Well, it all comes down to risk management. Back in the early ‘90s, financial markets were becoming increasingly complex, and investors needed a way to measure and manage risk. The VIX provided a solution by giving them a clear, quantifiable measure of market volatility.
And let’s be honest, the ‘90s were a pretty wild time for the markets. We had the dot-com boom, the Asian financial crisis, and plenty of other craziness. The VIX was like a lifeline for investors trying to navigate those turbulent waters.
How is the VIX Calculated?
Okay, let’s get a little nerdy for a moment. The VIX is calculated using a complex formula that involves options prices on the S&P 500 index. Don’t worry if that sounds like gibberish—let me break it down for you.
Basically, the VIX looks at the prices of options contracts that expire in the next 30 days. These prices reflect what traders are willing to pay to protect themselves against market moves. The higher the prices, the higher the expected volatility, and vice versa.
Here’s a quick rundown of the key steps in the calculation:
- Gather data on S&P 500 options prices.
- Calculate the implied volatility for each option.
- Combine the volatilities to get a single number—the VIX.
Now, I know what you’re thinking: “Do I really need to know all this math?” Probably not. Most traders and investors just look at the VIX number and use it as a guide. But if you’re the curious type, it’s always good to have a basic understanding of how it works.
The Role of VIX in Financial Markets
So, what exactly does the VIX do for the financial markets? Think of it as a barometer for investor sentiment. When the VIX is high, it usually means that investors are feeling nervous and uncertain about the future. On the other hand, a low VIX suggests that everyone is feeling pretty good about things.
But the VIX isn’t just a mood ring for the markets. It’s also a powerful tool for risk management. Traders use it to hedge their portfolios against potential losses. For example, if you’re worried about a market downturn, you can buy options that will pay off if the VIX spikes. It’s like buying insurance for your investments.
Who Uses the VIX?
The VIX is used by a wide range of market participants, from individual investors to institutional traders. Here are a few examples:
- Hedge Funds: These guys use the VIX to manage risk and protect their portfolios.
- Day Traders: They often use the VIX to time their trades, buying when the VIX is low and selling when it’s high.
- Institutional Investors: Large firms use the VIX to gauge market sentiment and adjust their strategies accordingly.
So, whether you’re a seasoned pro or a newbie, the VIX can be a valuable tool in your investment arsenal.
Using the VIX for Trading
Now, let’s talk about how you can actually use the VIX in your trading strategy. There are several ways to trade the VIX, and each has its own pros and cons. Here are a few popular methods:
1. VIX Futures
VIX futures allow you to bet on the future level of the VIX. If you think volatility is going to increase, you can buy a futures contract. If you think it’s going to decrease, you can sell one. It’s a bit like gambling, but with a lot more math involved.
2. VIX Options
VIX options give you the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the VIX at a certain price. They’re a bit more flexible than futures, but they can also be more complicated. Still, they’re a great way to hedge your portfolio or speculate on market moves.
3. VIX ETFs
If you’re not into the whole futures and options thing, you can always invest in a VIX ETF. These funds track the performance of the VIX and allow you to gain exposure without having to deal with the complexities of derivatives.
Now, keep in mind that trading the VIX can be risky. The market can be unpredictable, and things can change in the blink of an eye. So, always do your homework and make sure you understand the risks before diving in.
The Impact of VIX on Investor Sentiment
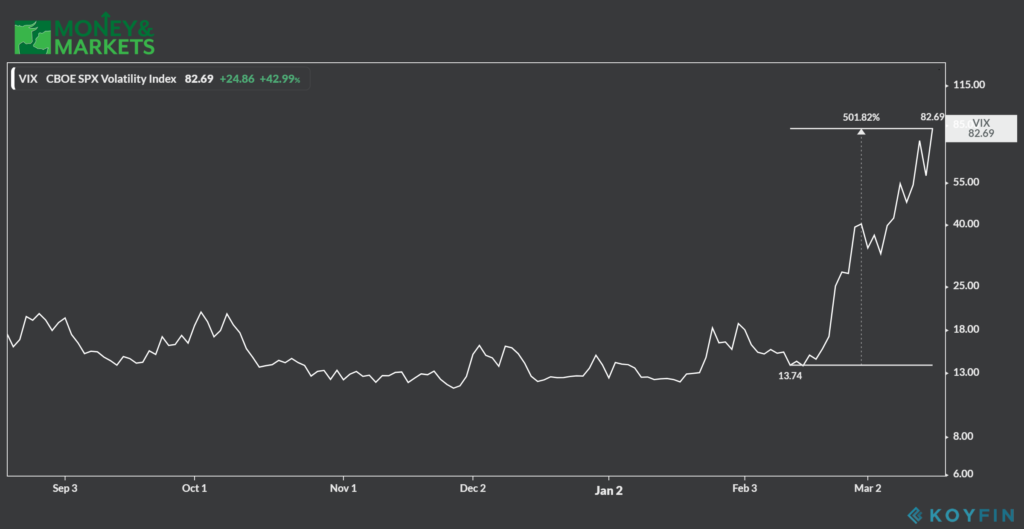
Let’s talk about how the VIX affects investor sentiment. As I mentioned earlier, the VIX is often referred to as the “fear gauge” because it tends to spike when investors are feeling anxious. But what exactly does that mean for the markets?
Well, when the VIX is high, it usually leads to a sell-off in stocks. Investors start dumping their holdings and moving into safer assets like bonds or gold. This can create a feedback loop where the sell-off causes even more fear, which drives the VIX even higher.
On the flip side, a low VIX can lead to complacency. Investors may start taking on more risk, thinking that everything is fine. But as we’ve seen in the past, that can lead to some nasty surprises when the market takes a turn for the worse.
How to Use VIX as a Sentiment Indicator
So, how can you use the VIX to gauge investor sentiment? Here are a few tips:
- Watch for spikes in the VIX. If it suddenly jumps, it could be a sign that the market is getting nervous.
- Look for trends. A consistently rising VIX could indicate growing uncertainty, while a falling VIX might suggest increasing confidence.
- Compare the VIX to other indicators. For example, if the VIX is high but economic data is strong, it could mean that the market is overreacting.
By paying attention to the VIX, you can get a better sense of what’s going on in the market and make more informed decisions.
Why VIX is Called the Fear Gauge
Alright, let’s address the elephant in the room. Why is the VIX often referred to as the “fear gauge”? Well, it all comes down to human psychology. When investors are feeling scared, they tend to flock to safe-haven assets like gold and bonds. This causes a drop in stock prices, which in turn drives up the VIX.
But it’s not just about fear. The VIX can also reflect excitement or euphoria. For example, during a bull market, the VIX tends to be low because investors are feeling confident and optimistic. So, while the “fear gauge” nickname is catchy, it’s only part of the story.
The Psychology of the VIX
Understanding the psychology behind the VIX can help you become a better investor. Here are a few key points to keep in mind:
- Investors are emotional creatures. Fear and greed can drive markets in ways that don’t always make sense.
- The VIX can be a leading indicator of market moves. If it starts to rise, it could be a warning sign that things are about to get rough.
- Don’t let the VIX scare you. While it’s a valuable tool, it’s not a crystal ball. Use it as one piece of the puzzle, not the whole picture.
By keeping these points in mind, you can use the VIX to your advantage without letting it control your emotions.
Strategies for Leveraging the VIX
Now that you know what the VIX is and how it works, let’s talk about how you can use it in your investment strategy. Here are a few strategies to consider:
1. Hedging with the VIX
If you’re worried about a market downturn, you can use the VIX to hedge your portfolio. For example, you could buy VIX futures or options to protect yourself against losses. It’s like buying insurance for your investments.
2.